The safety of MenQuadfi has been evaluated in more than 10,000 trial participants 6 weeks of age and older1
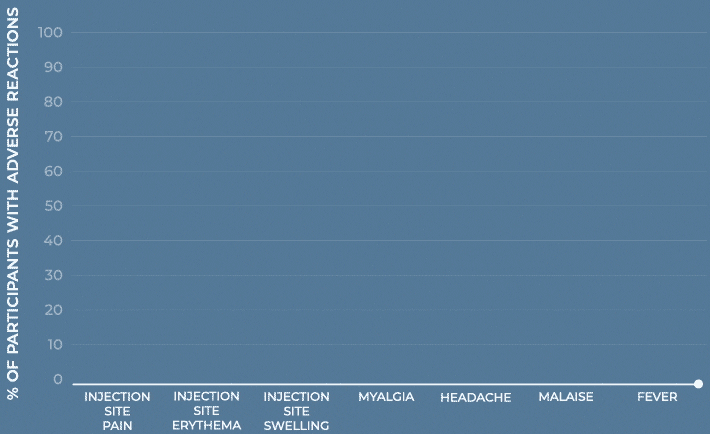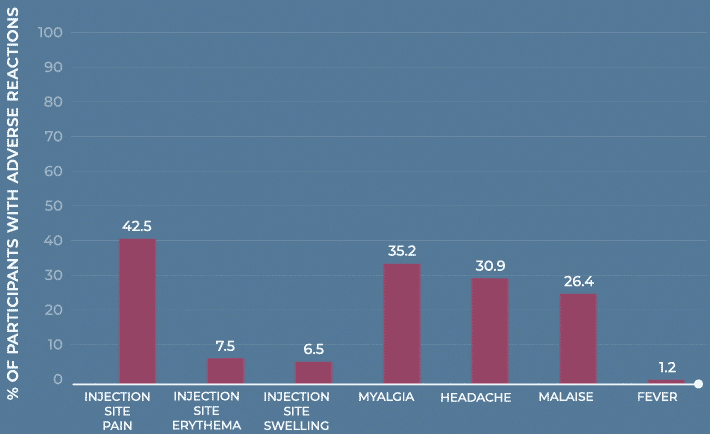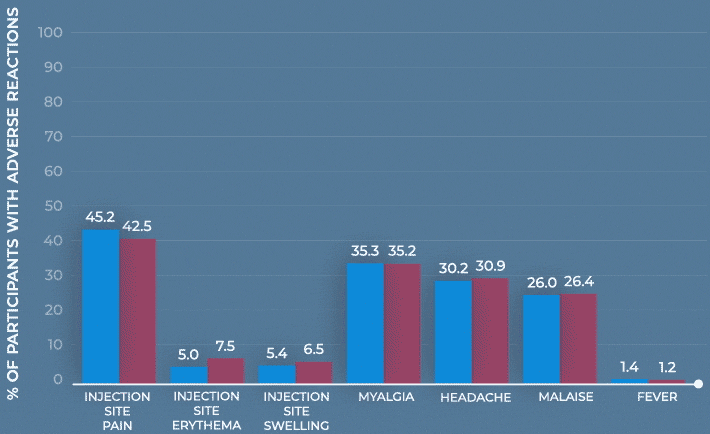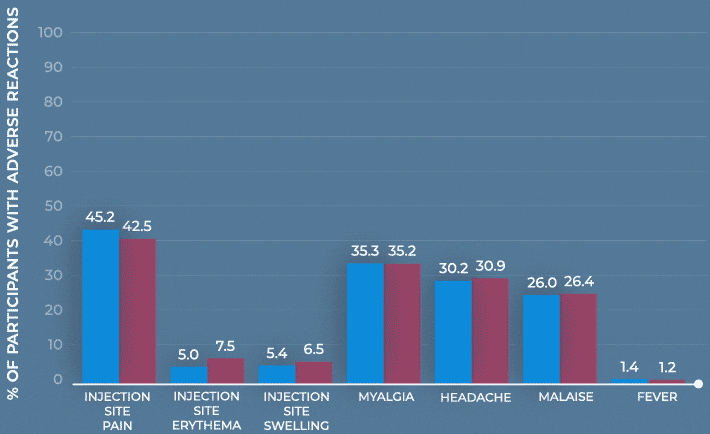
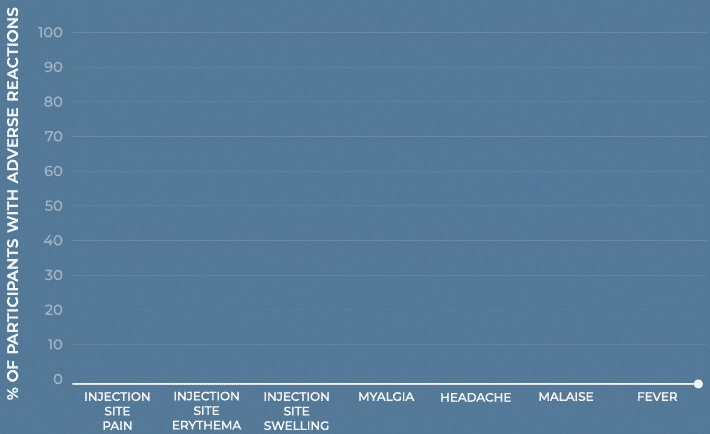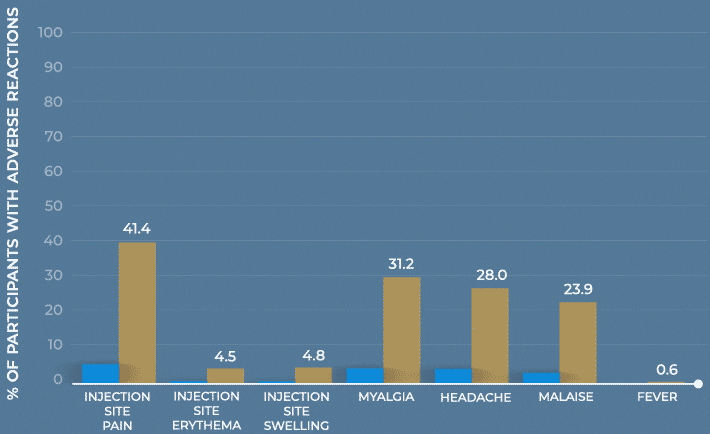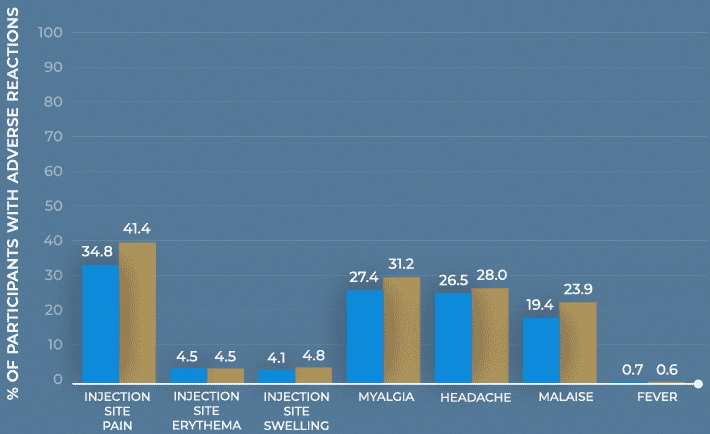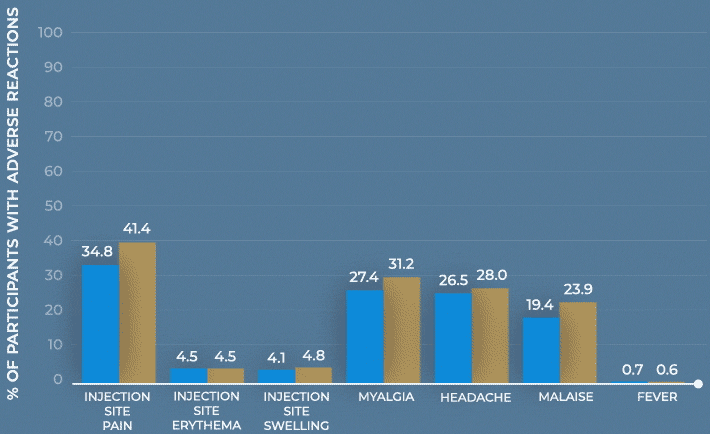
Study design: The immunogenicity and safety of MenQuadfi in adolescents 10 through 17 years of age were evaluated in a randomized, head-to-head clinical trial vs Menveo. Analyses included more than 900 participants. Solicited injection-site and systemic reactions were recorded by participants daily for 7 days following vaccination. All unsolicited adverse events that occurred within 30 days following vaccination were recorded by participants and collected at the next visit, and all serious adverse events were collected for at least 6 months after vaccination.1
Frequency of solicited injection-site reactions and systemic adverse reactions within 7 days after vaccination with MenQuadfi or Menveo1


Study design: The immunogenicity and safety of MenQuadfi were evaluated in a randomized, head-to-head clinical trial vs Menactra that included individuals 10 to 55 years of age (N=3344). Analyses were stratified by age, including a subpopulation consisting of nearly 1400 adolescents 10 through 17 years of age. Solicited injection-site and systemic reactions were recorded by participants daily for 7 days following vaccination. All unsolicited adverse events that occurred within 30 days following vaccination were recorded by participants and collected at the next visit, and all serious adverse events were collected for at least 6 months after vaccination.1-3
Frequency of solicited injection-site reactions and systemic adverse reactions within 7 days after vaccination with MenQuadfi or Menactra1

MenQuadfi should not be administered to anyone who has had a severe allergic reaction to any component of the vaccine, or after a previous dose of MenQuadfi or any other tetanus toxoid-containing vaccine.
Appropriate medical treatment must be immediately available to manage potential anaphylactic reactions following administration of MenQuadfi.
Some individuals with altered immunocompetence, including some receiving immunosuppressant therapy, may have reduced immune responses to MenQuadfi. Persons with certain complement deficiencies and those receiving treatment that inhibits terminal complement activation (eg, eculizumab) are at increased risk for invasive disease caused by N meningitidis, including serogroups A, C, W, and Y, even if they develop antibodies following vaccination with MenQuadfi.
Syncope (fainting) may occur in association with administration of injectable vaccines, including MenQuadfi. Procedures should be in place to avoid injury from fainting.
Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS) has been reported in temporal relationship following administration of another US-licensed meningococcal quadrivalent polysaccharide conjugate vaccine. The decision to give MenQuadfi to persons with a history of GBS should take into account the expected benefits and potential risks.
Immunization with MenQuadfi does not substitute for routine tetanus immunization.
Vaccination with MenQuadfi may not protect all vaccine recipients.
The most common adverse reactions following primary vaccination with MenQuadfi in infants 6 weeks through 23 months of age include tenderness, erythema, and swelling at the injection site; irritability, abnormal crying, drowsiness, appetite loss, fever, and vomiting. In individuals 2 years of age and older,the most common adverse reactions include pain at the injection site; myalgia, headache, and malaise. Other common adverse reactions in children 2 through 9 years of age include erythema and swelling at the injection site. In adolescents and adults, rates of solicited adverse reactions following a booster dose were comparable to those observed following primary vaccination. Other adverse reactions may occur.
Please see the full Prescribing Information for MenQuadfi.
Click here to learn more about Sanofi’s commitment to fighting counterfeit drugs.
MenACWY = N meningitidis serogroups A, C, W, and Y. *Menveo (Meningococcal [Groups A, C, Y, and W-135] Oligosaccharide Diphtheria CRM197 Conjugate Vaccine). †Menactra (Meningococcal [Groups A, C, Y, and W-135] Polysaccharide Diphtheria Toxoid Conjugate Vaccine).
MenQuadfi is a registered trademark of Sanofi Inc.
Menactra is a registered trademark of Sanofi, its affiliates, and its subsidiaries.
The other brands listed are trademarks owned by or licensed to their respective owners and are not owned by or licensed to Sanofi, its affiliates and/or its subsidiaries.